Some simple codes about Landauer-Buttiker formula.
Landauer-Buttiker formalism为Ii=he2∑j=i[TjiVi−TijVj],无论系统的时间反演是否破缺,该公式都成立。
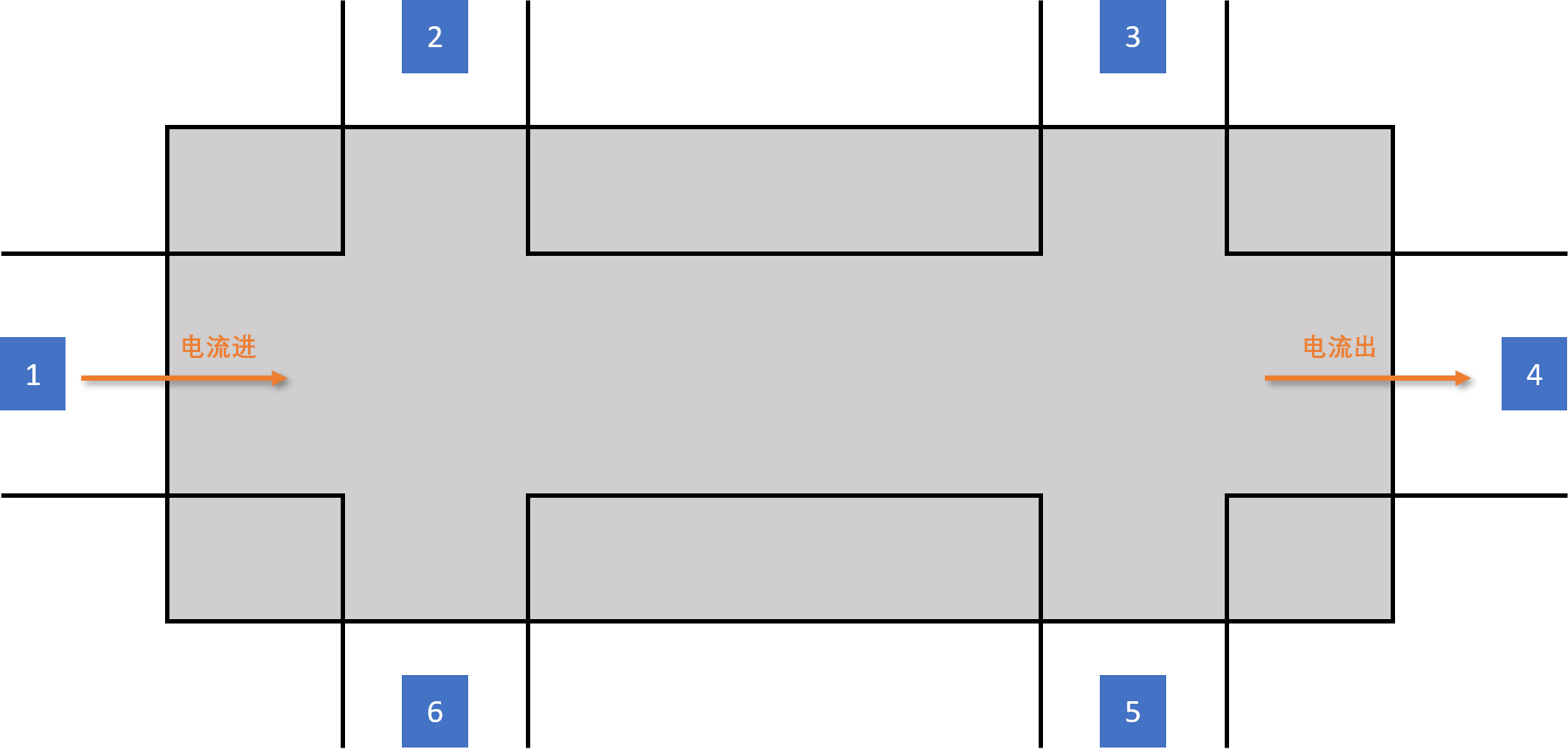
在这里,我们采用的是六电极的构型(如下图 所示),并且约定:电流端为1和4,电流1进4出,即I1=−I4=I,而其它电极(2,3,5,6)则作为电压端,不通电流,即I2=I3=I5=I6=0,那么将Landauer-Buttiker公式写成矩阵的形式应为:
I00−I00=he2∑i=1Ti1−T21−T31−T41−T51−T61−T12∑i=2Ti2−T32−T42−T52−T62−T13−T23∑i=3Ti3−T43−T53−T63−T14−T24−T34∑i=4Ti4−T54−T64−T15−T25−T35−T45∑i=5Ti5−T65−T16−T26−T36−T46−T56∑i=6Ti6V1V2V3V4V5V6
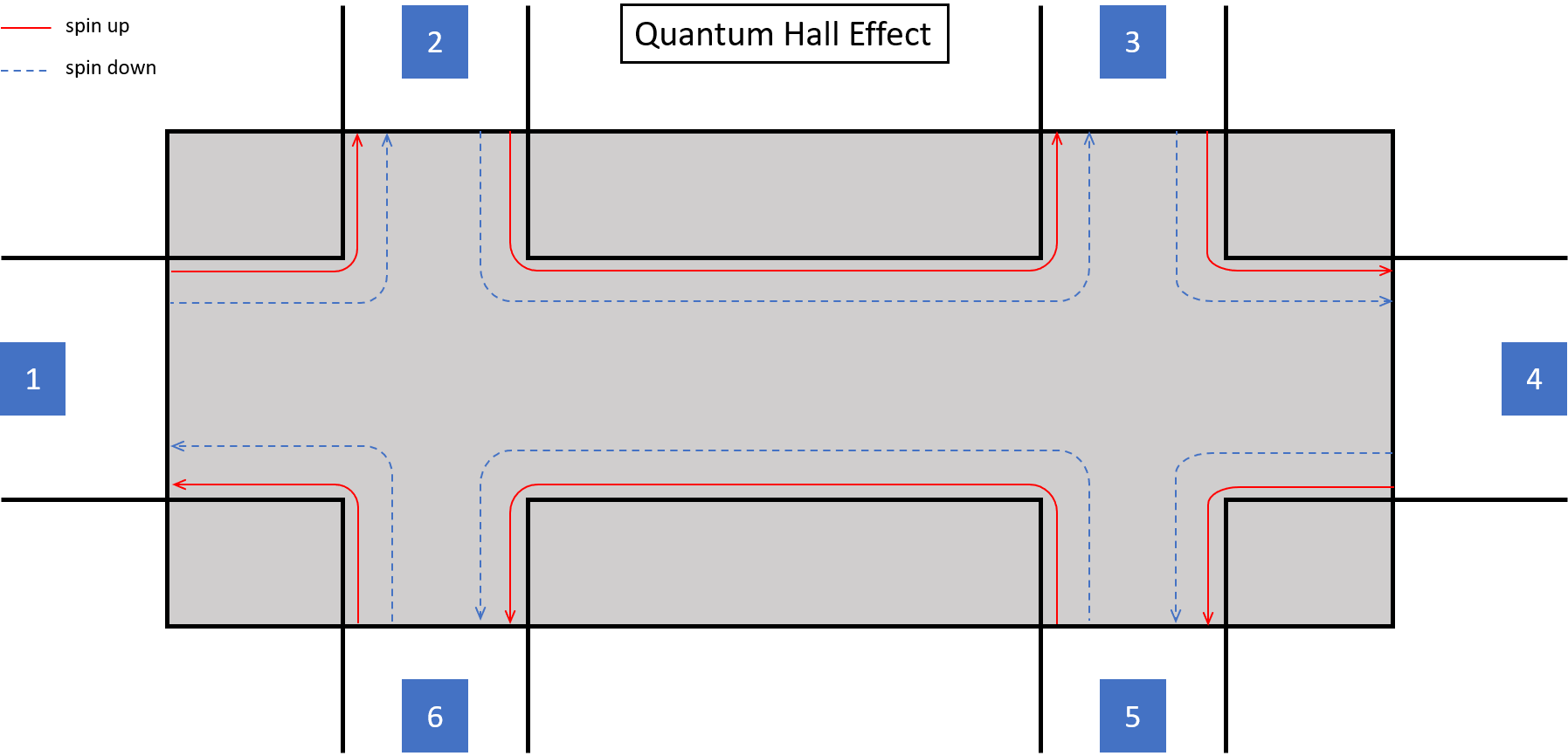
2. Quantum Hall Effect
QHE的六电极构型如下图 所示,在这里我们考虑自旋向上和自旋向下两个通道。在QHE中,在边缘处所有边界态的运动方向都是一致的,这样的边界态也被称为chiral edge state。
在QHE的六电极构型中,只有相邻的两个电极之间有直接的电子传递,并且由于具有手性,6电极中的电子只能沿着两个通道(红色实线和蓝色虚线)运动到1电极,
同理,
1电极中的电子只能沿着两个通道(红色实线和蓝色虚线)运动到2电极,
2电极中的电子只能沿着两个通道(红色实线和蓝色虚线)运动到3电极,
3电极中的电子只能沿着两个通道(红色实线和蓝色虚线)运动到4电极,
4电极中的电子只能沿着两个通道(红色实线和蓝色虚线)运动到5电极,
5电极中的电子只能沿着两个通道(红色实线和蓝色虚线)运动到6电极,
因此其T矩阵的矩阵元为:
T16=2,T21=2,T32=2,T43=2,T54=2,T65=2,
其它矩阵元均为0,代入Landauer-Buttiker的矩阵公式中有
I00−I00=he22−2000002−2000002−2000002−2000002−2−200002V1V2V3V4V5V6
通过高斯消元法,可以将这个方程组化简为:
0.5I0.5I0.5I000=he2100000010000001000000100000010−1−1−1−1−10V1V2V3V4V5V6
根据该方程组,可以很容易得到:
he2(V1−V4)=0.5I,(V2−V3)=0,(V6−V5)=0,he2(V2−V6)=0.5I,he2(V3−V5)=0.5I
可以发现四端法纵向电阻为零,R14,23=R14,65=0,但是在两端法下纵向电导并不为零,为2倍量子电导G14,14=2he2,而对于四端法横向电导则为两倍量子电导,G14,26=G14,35=2he2。
LB code for QHE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
| n_terminal = 6;
current_in = 1;
current_out = 4;
I = zeros(n_terminal, 1);
I(current_in) = 1;
I(current_out) = -1;
T = zeros(n_terminal);
for i = 1:n_terminal
T(i,i) = 2;
next = rem(5+i, n_terminal);
if next == 0
T(i, next + n_terminal) = -2;
else
T(i, next) = -2;
end
end
G = [T,I];
vec_temp = zeros(1, n_terminal+1);
for i = 1:(n_terminal-1)
if G(i,i) == 0
for ii = (i+1):n_terminal
if ~(G(ii, i) == 0)
vec_temp = G(ii, :);
G(ii, :) = G(i, :);
G(i, :) = vec_temp;
break
end
end
end
if G(i, i) == 0
continue
end
for j = (i+1):n_terminal
if ~(G(j,i) == 0)
ratio = G(j,i) / G(i,i);
G(j,:) = G(j,:) - ratio * G(i,:);
end
end
end
for i = n_terminal:-1:2
if abs(G(i,i)) < 1e-8
continue
end
G(i, :) = G(i, :) / G(i, i);
for j = (i-1):-1:1
if ~(G(j,i) == 0)
ratio = G(j,i);
G(j,:) = G(j,:) - ratio * G(i,:);
end
end
end
G(1, :) = G(1, :) / G(1, 1);
v_left = 2;
v_right = 3;
ratio = G(v_right, end-1) / G(v_left, end-1);
if abs(abs(ratio)-1) > 1e-8
disp("some problems")
end
delta_G = G(v_right, end) - G(v_left, end);
|
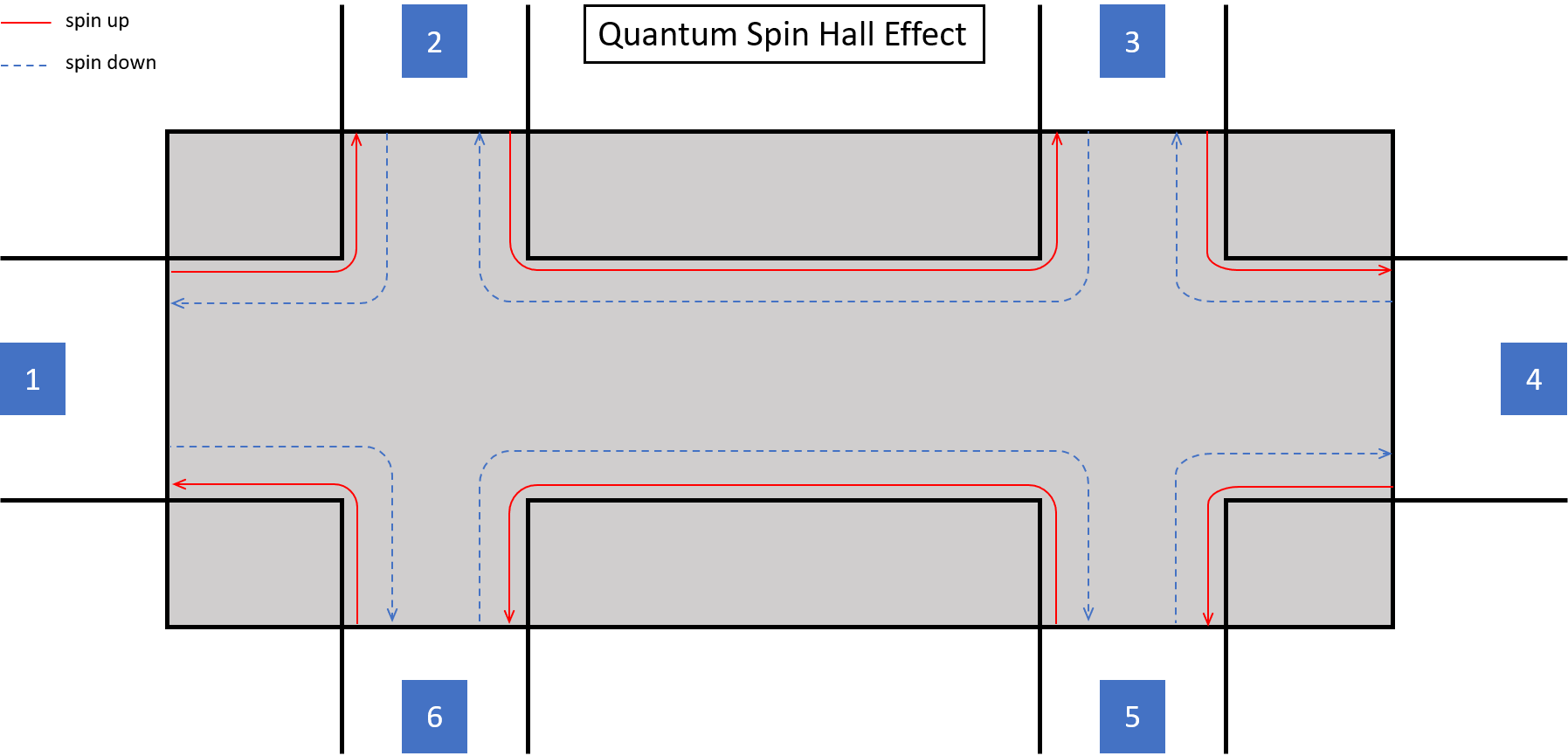
3. Quantum Spin Hall Effect
QSHE的六电极构型如下图 所示,在这里我们考虑自旋向上和自旋向下两个通道。在QSHE中,在边缘处自旋向上与自旋向下的边界态的运动方向是相反的,这体现了系统的时间反演对称性,而这样的边界态也被称为helical edge state。
在QSHE的六电极构型中,只有相邻的两个电极之间有直接的电子传递,并且由于是helical edge state,
6电极中的电子可以沿着一个通道(红色实线)边缘运动到1电极,而沿着另一个通道(蓝色虚线)边缘运动到5电极,
同理,
1电极中的电子可以沿着一个通道(红色实线)边缘运动到2电极,而沿着另一个通道(蓝色虚线)边缘运动到6电极,
2电极中的电子可以沿着一个通道(红色实线)边缘运动到3电极,而沿着另一个通道(蓝色虚线)边缘运动到1电极,
3电极中的电子可以沿着一个通道(红色实线)边缘运动到4电极,而沿着另一个通道(蓝色虚线)边缘运动到2电极,
4电极中的电子可以沿着一个通道(红色实线)边缘运动到5电极,而沿着另一个通道(蓝色虚线)边缘运动到3电极,
5电极中的电子可以沿着一个通道(红色实线)边缘运动到6电极,而沿着另一个通道(蓝色虚线)边缘运动到4电极,
因此其T矩阵的矩阵元为:
T61=T16=1,T21=T12=1,T32=T23=1,T43=T34=1,T45=T54=1,T56=T65=1
其它矩阵元均为0,代入Landauer-Buttiker的矩阵公式中有:
I00−I00=he22−1000−1−12−10000−12−10000−12−10000−12−1−1000−12V1V2V3V4V5V6
通过高斯消元法,可以将这个方程组化简为:
0.5I0−0.5I−I−0.5I0=he2100000010000001000000100000010−1−1−1−1−10V1V2V3V4V5V6
根据该方程组,可以很容易得到:
he2(V1−V4)=1.5I,he2(V2−V3)=0.5I,he2(V6−V5)=0.5I,(V2−V6)=0,(V3−V5)=0
可以发现四端法纵向电导为两倍量子电导,G14,23=G14,65=2he2
两端法纵向电导为32倍量子电导 G14,14=32he2
而对于四端法横向电阻则都为零,R14,26=R14,35=0
LB code for QSHE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
| n_terminal = 6;
current_in = 1;
current_out = 4;
I = zeros(n_terminal, 1);
I(current_in) = 1;
I(current_out) = -1;
T = zeros(n_terminal);
for i = 1:n_terminal
T(i,i) = 2;
left = rem(i-1, n_terminal);
right = rem(i+1, n_terminal);
if left == 0
T(i, left + n_terminal) = -1;
else
T(i, left) = -1;
end
if right == 0
T(i, right + n_terminal) = -1;
else
T(i, right) = -1;
end
end
G = [T,I];
vec_temp = zeros(1, n_terminal+1);
for i = 1:(n_terminal-1)
if G(i,i) == 0
for ii = (i+1):n_terminal
if ~(G(ii, i) == 0)
vec_temp = G(ii, :);
G(ii, :) = G(i, :);
G(i, :) = vec_temp;
break
end
end
end
if G(i, i) == 0
continue
end
for j = (i+1):n_terminal
if ~(G(j,i) == 0)
ratio = G(j,i) / G(i,i);
G(j,:) = G(j,:) - ratio * G(i,:);
end
end
end
for i = n_terminal:-1:2
if abs(G(i,i)) < 1e-8
continue
end
G(i, :) = G(i, :) / G(i, i);
for j = (i-1):-1:1
if ~(G(j,i) == 0)
ratio = G(j,i);
G(j,:) = G(j,:) - ratio * G(i,:);
end
end
end
G(1, :) = G(1, :) / G(1, 1);
v_left = 2;
v_right = 3;
ratio = G(v_right, end-1) / G(v_left, end-1);
if abs(abs(ratio)-1) > 1e-8
disp("some problems")
end
delta_G = G(v_right, end) - G(v_left, end);
|
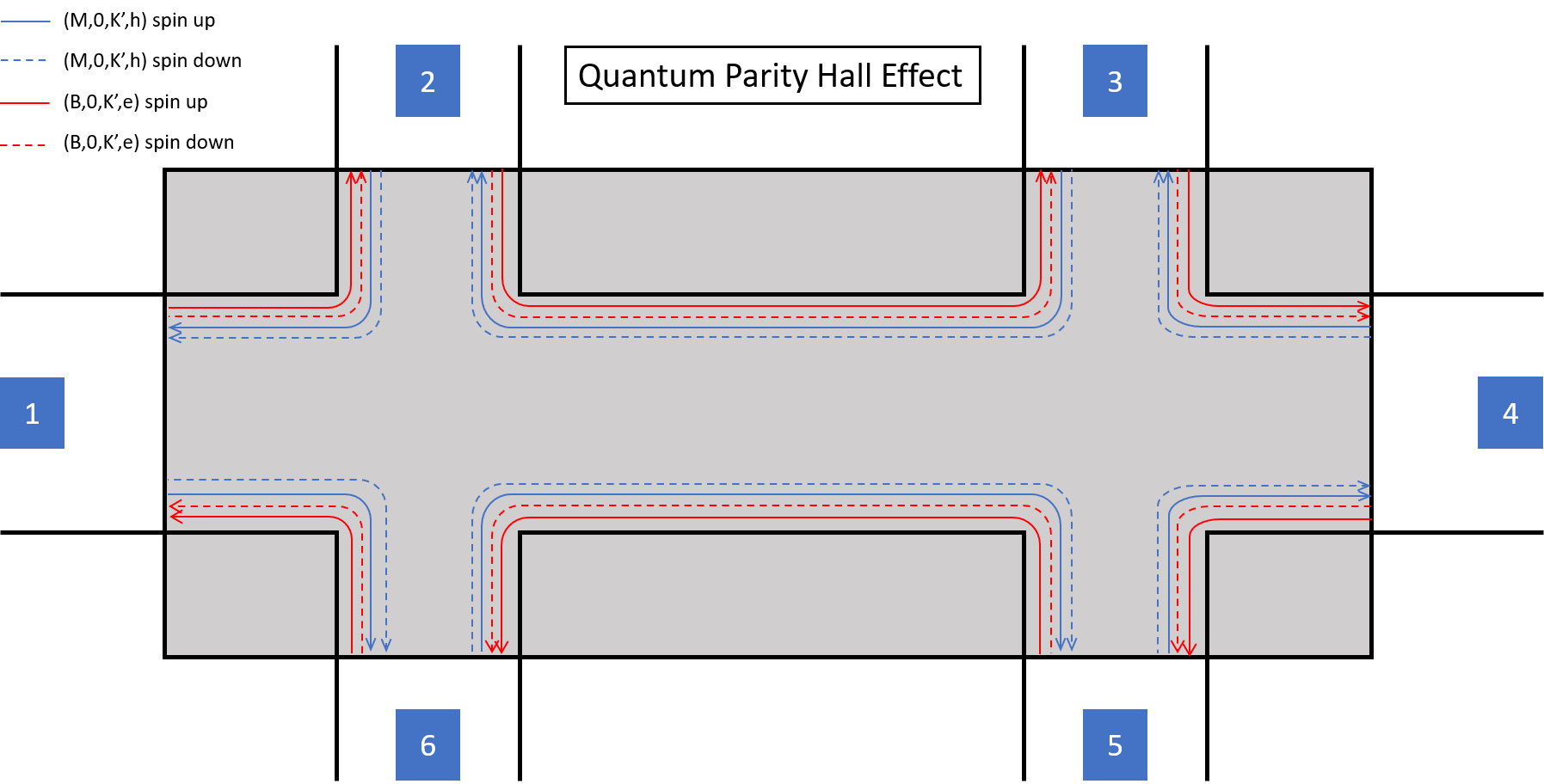
4. Quantum Parity Hall Effect
QPHE的六电极构型如下图 所示,在这里需要考虑四个通道,其中两个是来自自旋简并的单层石墨烯中空穴型朗道能级,
另外两个则是来自自旋简并的双层石墨烯中电子型朗道能级。
在QPHE中,在边缘处来自单层与来自双层的边界态的运动方向是相反的,这是因为一个是空穴型另一个是电子型的缘故,但每个朗道能级中自旋向上和
自旋向下的边界态的运动方向是一致的,这样的边界态也被称为helical edge state,但是与QSHE不同,这里是单层与双层的边界态运动方向不同
而不是自旋相反的边界态运动方向不同,它破坏了时间反演对称性,但是受到了镜面对称性的保护。
在QPHE的六电极构型中,只有相邻的两个电极之间有直接的电子传递,并且由于是helical edge state,
6电极中的电子可以沿着两个通道(红色实线和红色虚线)边缘运动到1电极,而沿着另两个通道(蓝色实线和蓝色虚线)边缘运动到5电极,
同理,
1电极中的电子可以沿着两个通道(红色实线和红色虚线)边缘运动到2电极,而沿着另两个通道(蓝色实线和蓝色虚线)边缘运动到6电极,
2电极中的电子可以沿着两个通道(红色实线和红色虚线)边缘运动到3电极,而沿着另两个通道(蓝色实线和蓝色虚线)边缘运动到1电极,
3电极中的电子可以沿着两个通道(红色实线和红色虚线)边缘运动到4电极,而沿着另两个通道(蓝色实线和蓝色虚线)边缘运动到2电极,
4电极中的电子可以沿着两个通道(红色实线和红色虚线)边缘运动到5电极,而沿着另两个通道(蓝色实线和蓝色虚线)边缘运动到3电极,
5电极中的电子可以沿着两个通道(红色实线和红色虚线)边缘运动到6电极,而沿着另两个通道(蓝色实线和蓝色虚线)边缘运动到4电极,
因此其T矩阵的矩阵元为:
T61=T16=2,T21=T12=2,T32=T23=2,T43=T34=2,T45=T54=2,T56=T65=2
其它矩阵元均为0,代入Landauer-Buttiker的矩阵公式中有:
I00−I00=he24−2000−2−24−20000−24−20000−24−20000−24−2−2000−24V1V2V3V4V5V6
通过高斯消元法,可以将这个方程组化简为:
0.25I0−0.25I−0.5I−0.25I0=he2100000010000001000000100000010−1−1−1−1−10V1V2V3V4V5V6
根据该方程组,可以很容易得到:
he2(V1−V4)=0.75I,he2(V2−V3)=0.25I,he2(V6−V5)=0.25I,(V2−V6)=0,(V3−V5)=0
可以发现四端法纵向电导为四倍量子电导,G14,23=G14,65=4he2
两端法纵向电导为34倍量子电导 G14,14=34he2
而对于四端法横向电阻则都为零,R14,26=R14,35=0
LB code for QPHE
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
| n_terminal = 6;
current_in = 1;
current_out = 4;
I = zeros(n_terminal, 1);
I(current_in) = 1;
I(current_out) = -1;
T = zeros(n_terminal);
for i = 1:n_terminal
T(i,i) = 4;
left = rem(i-1, n_terminal);
right = rem(i+1, n_terminal);
if left == 0
T(i, left + n_terminal) = -2;
else
T(i, left) = -2;
end
if right == 0
T(i, right + n_terminal) = -2;
else
T(i, right) = -2;
end
end
G = [T,I];
vec_temp = zeros(1, n_terminal+1);
for i = 1:(n_terminal-1)
if G(i,i) == 0
for ii = (i+1):n_terminal
if ~(G(ii, i) == 0)
vec_temp = G(ii, :);
G(ii, :) = G(i, :);
G(i, :) = vec_temp;
break
end
end
end
if G(i, i) == 0
continue
end
for j = (i+1):n_terminal
if ~(G(j,i) == 0)
ratio = G(j,i) / G(i,i);
G(j,:) = G(j,:) - ratio * G(i,:);
end
end
end
for i = n_terminal:-1:2
if abs(G(i,i)) < 1e-8
continue
end
G(i, :) = G(i, :) / G(i, i);
for j = (i-1):-1:1
if ~(G(j,i) == 0)
ratio = G(j,i);
G(j,:) = G(j,:) - ratio * G(i,:);
end
end
end
G(1, :) = G(1, :) / G(1, 1);
v_left = 2;
v_right = 3;
ratio = G(v_right, end-1) / G(v_left, end-1);
if abs(abs(ratio)-1) > 1e-8
disp("some problems")
end
delta_G = G(v_right, end) - G(v_left, end);
|